The Glycemic Index is a measure of how quickly certain foods can raise blood sugar levels. This scale is an essential tool for anyone who wants to maintain a balanced and healthy diet.
- Foods with a low glycemic index (GI) are digested more slowly and release glucose gradually into the bloodstream, providing a steady supply of energy that lasts longer.
- In contrast, foods with a high GI are digested quickly, leading to a rapid spike in blood sugar levels followed by a crash.
When it comes to weight loss, the glycemic index (GI) is a critical piece of information to keep in mind. Unlike fad diets that restrict entire food groups, the GI method focuses on the quality of carbohydrates consumed.
Research has shown that consuming foods with a high Glycemic Index can lead to weight gain while consuming foods with a low GI can aid in weight loss. This is because high-GI foods can lead to insulin resistance which makes it harder for the body to burn fat. On the other hand, foods with a low GI can help regulate insulin levels and promote fat burning.
Incorporating low-GI foods into your diet is relatively easy. Some examples of low-GI foods include sweet potatoes, quinoa, brown rice, berries, nuts, and vegetables like spinach and broccoli. These foods are not only good for weight loss but also provide several health benefits such as reducing the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
Table of Contents
However, it is important to note that the GI is not the only factor that affects weight loss. It is still essential to consume a well-balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Also, portion control is crucial, even when eating low-GI foods.
The glycemic index is a numerical ranking system that measures how quickly carbohydrates in food raise blood glucose levels. Foods with high GI scores tend to cause a spike in blood sugar levels, leading to a release of insulin to combat it. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body move glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy or storage as fat.
The higher the glycemic index, the greater the insulin response and the more likely it is that excess calories will get stored as fat.
In terms of weight loss, the evidence for the low-GI diet is mixed. Some studies have shown that a low-GI diet can lead to weight loss, while others have not found a significant difference between low-GI diets and other diets.
However, the low-GI diet does have some advantages over other diets. For example, low-GI foods tend to be more filling and nutrient-dense which can result in eating less overall.
While a low-GI diet can be effective, it should not be the only dietary consideration. It is essential to maintain a balanced diet including a variety of low-GI foods, fruits, vegetables, protein, and healthy fats. The total amount of carbohydrates in a meal or snack can also affect blood sugar levels so it is important to moderate portions and macronutrient balance.
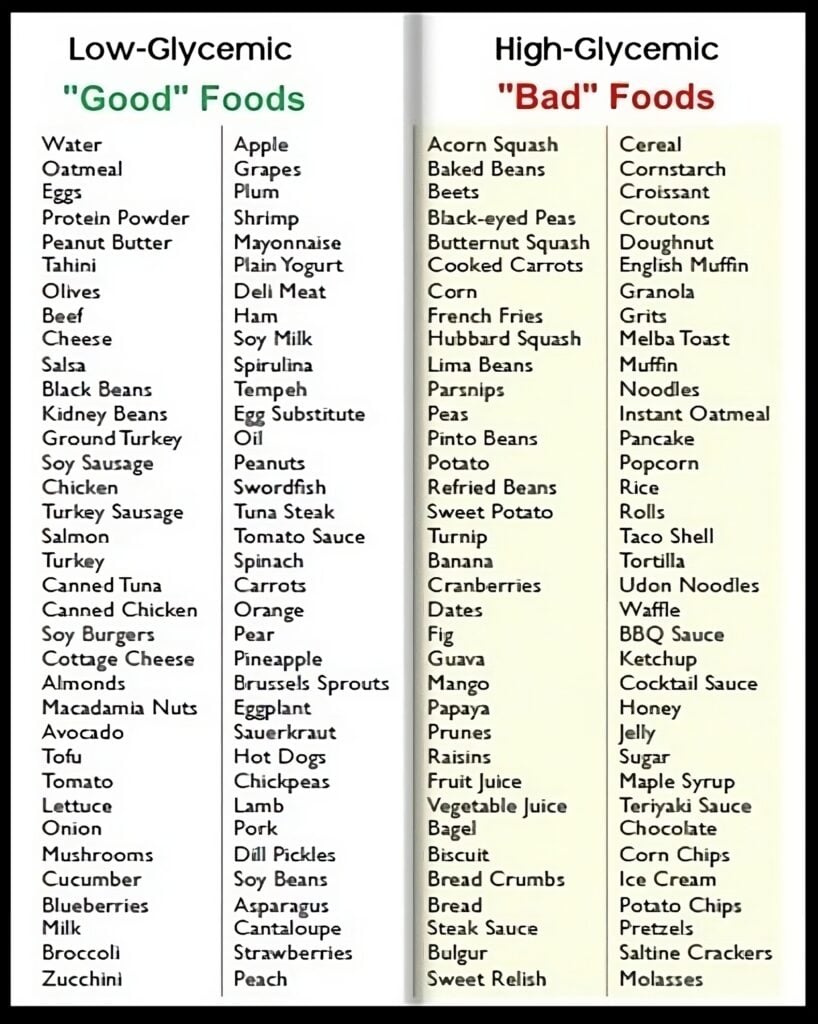
How Does Glycemic Index Affect Weight Loss?
Eating a diet that’s high in refined carbohydrates like white bread, sugary drinks, and processed snacks is one reason people struggle to lose weight. Such foods carry a high glycemic index, which means they cause a quick spike in blood sugar, leading to insulin being released and calories being stored as fat.
In contrast, including low-GI foods such as leafy greens, legumes, nuts, and whole grains can help keep insulin levels stable, preventing excess calories from being stored. Choosing low-GI foods can also help reduce hunger and keep you feeling full, making it easier to stick to your weight loss goals.
Although the glycemic index is a useful tool for understanding how different foods impact blood sugar levels, it doesn’t tell the whole story. Glycemic load refers to the total amount of carbohydrates in a serving of food multiplied by the GI score. This adjusts for the fact that some high-GI foods, like watermelon, have a low glycemic load since they have a low carb content overall.
On the other hand, some low-GI foods like carrots may still have a high glycemic load because they have a higher carb content in the serving size. Therefore, it is essential to consider both the glycemic index and glycemic load when making dietary decisions.
Tips for Incorporating Low-GI Foods
Incorporating low-GI foods into your diet can be easy with some planning and preparation. Start by swapping out high GI foods for low GI alternatives such as brown rice instead of white, sweet potato instead of regular potato, and replacing typical snacks like chips and candy with nuts and seeds.
Another key aspect is to balance your meals with low-GI foods that are high in fiber and protein. This will help slow down digestion and keep you feeling full for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Demystifying the Connection between High Glycemic Foods and Belly Fat
The key to managing your weight and health is balance. It is important to understand that not all high glycemic foods are created equal and the impact on your body depends on factors such as portion size, overall diet quality, and physical activity levels.
One way to enjoy high-glycemic foods in moderation is to combine them with low-glycemic foods. For example, instead of eating a bag of chips, pair them with hummus or guacamole to add some healthy fat and protein. This will slow down the digestion process and prevent the blood sugar spike that can lead to belly fat.
You can also opt for whole grain alternatives to white bread or rice since whole grains are digested slower and contain more fiber which helps keep you feeling full for longer.
It is important to note that belly fat can also be caused by a range of other factors such as stress, lack of sleep, and genetics. Therefore, focusing solely on reducing your intake of high-glycemic foods may not be the only solution to managing your weight and overall health.
Other impacts of glycemic index on metabolism
Beyond its impact on weight and blood sugar, glycemic index can also impact hunger levels and overall energy levels. When consuming high-GI foods, you may experience a sudden spike in energy followed by a crash leading you to feelings of exhaustion and hunger.
In contrast, low GI foods provide more sustained and stable energy levels, helping to prevent hunger pangs and energy slumps.
What are the benefits of a low-glycemic diet?
There is a growing body of research that suggests that low-glycemic diets can provide various health benefits.
- Aiding in weight loss: Low GI foods can increase satiety, reduce hunger, and promote fat burning, leading to a reduction in calorie intake and weight loss.
- Regulating blood sugar levels: Low GI foods can reduce blood sugar spikes and dips, prevent insulin resistance, and lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Improving cardiovascular health: Low GI foods can decrease inflammation, improve blood lipid profiles, and lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.
What are the drawbacks of a low-glycemic diet?
While low-glycemic diets can be beneficial for many people, they are not without drawbacks. Some potential concerns of a low-glycemic diet include:
- Low GI foods are not always readily available or appealing to some people which can limit their dietary diversity and enjoyment.
- Low GI diets often involve reducing carbohydrate intake which can lead to nutrient deficiencies, muscle loss, and low energy levels, especially in athletes or active individuals.
- The GI values of foods can vary depending on individual factors such as cooking methods, ripeness, and combinations with other foods which can make it challenging to accurately follow a low-glycemic diet.
The Impact of Glycemic Index of Fruits on Your Weight Loss Journey
Low glycemic index fruits are those that have a GI score of less than 55. Consumption of low glycemic index fruits can help to lose weight effectively.
Apple, cherries, cranberries, grapefruit, kiwi, and oranges are some low glycemic index fruits that can be included in your weight loss diet. These fruits have a low glycemic index that slows down the digestive process and provides satiety for a more extended period.
Moderate glycemic index fruits include those that have a GI score between 55 to 69.
Blueberries, mangoes, figs, and papayas are some moderate glycemic index fruits that can be included in your diet. It is essential to note that consuming moderate glycemic index fruits may not be suitable for people with a diabetic history.
High glycemic index fruits have a GI score of more than 70.
If you’re trying to lose weight, avoid high glycemic index fruits such as bananas, watermelon, raisins, and dates. These fruits are also known to be high in calories which can lead to weight gain.
Kate Scarlata MPH, RDN
Registered Dietitian
https://www.katescarlata.com/about
Simmons University
https://www.linkedin.com/in/kate-scarlata-mph-rdn-441bb7b/
Popular Foods and Their GI Rankings
Fruits are a great source of nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber. However, not all fruits have the same effect on blood sugar levels. Here are some common fruits ranked by their GI scores:
With a GI of 72, watermelon is considered high GI. While watermelon does contain some vitamins and minerals, it is quite high in sugar and low in fiber. As a result, it is best to consume watermelon in moderation.
With a GI of 39 (out of 100), apples are classified as a low-GI food. Apples are also high in fiber and contain antioxidants that help reduce inflammation in the body. The fiber in apples also makes them great for digestion and heart health.
Bananas have a GI of 51, which is considered medium. Bananas are also a great source of potassium, which can help regulate blood pressure. However, they are also high in carbs (which can raise blood sugar levels) and low in fiber.
Pineapple has a GI score of 66, which is higher than many other fruits. However, it is also high in the enzyme bromelain, which can help with digestion and reduce inflammation in the body. Pineapple also contains high levels of Vitamin C and manganese.
Mangos have a medium GI score of 56. They are high in vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants. However, mangos are also high in sugar, so it is best to consume them in moderation.
Vegetables are low in carbohydrates and high in fiber making them a great option for those watching their blood sugar levels.
Best Fruits and Vegetables for Juicing
Low GI Vegetables
These vegetables have a GI score of 55 or lower, making them ideal for people who want to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Examples of these vegetables include asparagus, broccoli, carrots, lettuce, and tomatoes. Incorporating these vegetables into your diet can help you maintain healthy blood sugar levels, reduce your risk of diabetes, and keep you feeling energized throughout the day.
Medium GI Vegetables
These vegetables have a GI score of 56-69 and should be consumed in moderation. Examples include sweet potatoes, parsnips, peas, and corn. While they can have positive health benefits (such as being high in fiber and vitamins), the high GI value also means they can cause a rapid rise in blood sugar levels. People with diabetes who are watching their carbohydrate intake should especially take note of their consumption of medium GI vegetables.
High GI Vegetables
These vegetables score 70 or higher on the GI scale, which means they can cause a quick spike in blood sugar levels. Examples include potatoes (white), pumpkin, and beets. These vegetables should be consumed in moderation and always paired with a protein or high-fiber food, to help slow down the absorption of the high glycemic carbohydrates.
Leafy Greens
It’s important to note the GI of leafy greens, as their score is so low that you don’t need to worry about them affecting your blood sugar level in a negative way. These leafy greens include spinach, lettuce, and kale. In fact, consuming these vegetables can help regulate your blood sugar. They are low in calories but high in fiber, which slows down the absorption of other high-GI foods that you eat together with them.
Other Factors to Consider
While some vegetables like potatoes and carrots may have a high GI score, they are also packed with fiber and nutrients that are essential for good health. This is why it’s important to practice moderation and pair your high-GI vegetables with a protein or high-fiber food.
Grains are a staple in most people’s diets, but not all grains are created equal in terms of their effect on blood sugar.
Bulgur Wheat: with a GI score of 46, Bulgur Wheat is considered to have a low glycemic index and is a good choice for people who want to manage their blood sugar levels. This hearty and nutty grain is easy to prepare and can be used in salads, pilafs, and breakfast porridge.
Brown rice has a GI score of 50, and it is a great alternative to the white rice that we often consume. Brown rice is an excellent source of fiber and provides a slow release of energy that can keep you feeling full and energized for longer
Quinoa has a GI score of 53 and is an excellent source of plant-based protein, fiber, and essential minerals. This versatile grain has a fluffy texture and nutty flavor and can be used in salads, soups, and main dishes.
Barley has a GI score of 28 and is a great source of soluble fiber, which slows down digestion and promotes satiety. Barley is also beneficial for gut health as it helps in reducing the risk of colon cancer.
Whole wheat bread has a GI score of 69, which is still lower than white bread. It is a healthier choice for people with diabetes or those who want to manage blood sugar levels. Whole wheat bread is an excellent source of fiber and provides essential nutrients like B vitamins and iron.
Cornmeal has a GI score of 73 and is one of the highest glycemic index grains on our list. However, it is essential to note that cornmeal is consumed in small quantities and is often paired with foods that have a low GI score.
Dairy products are a good source of protein and calcium.
Low-GI Dairy Foods
Greek yogurt: Greek yogurt is an excellent source of protein and makes for a low-GI dairy option. With a GI score of 11, it is much lower in sugar than regular yogurt.
Cheese lovers, rejoice! Cheese is a low-GI dairy option that you can indulge in without any worries. Most types of cheese have a GI score of less than 55.
While butter is high in calories and should be consumed in moderation, it makes for a low-GI dairy option. With a GI score of zero, butter won’t cause a spike in your blood sugar levels.
Moderate-GI Dairy Foods
Regular cow’s milk has a moderate GI score of 41. If you’re looking for a low-GI option, consider switching to unsweetened almond milk, which has a GI score of just 0.
Ice cream is a popular dairy treat, and the good news is that it has a moderate GI score of 57. Look for ice creams that are low in added sugars to keep your blood sugar levels in check.
High-GI Dairy Foods
Flavored yogurt is high in sugar, which means it has a high GI score. A container of flavored yogurt can have a GI score of up to 70 or even higher. Opt for plain yogurt and add fresh fruit for a healthier option.
Condensed milk is high in sugar and has a GI score of 68. It is best to avoid this dairy product if you’re trying to manage your blood sugar levels.
Everybody has a craving for something sweet or salty from time to time.
Donuts – GI score: 76
Donuts are a popular breakfast pastry that can wreak havoc on your blood sugar levels. Their high sugar content and refined grains earn them a spot as the fast-food snack with the highest GI score. While it may be tempting to grab a donut in the morning, you may want to opt for a lower-GI breakfast instead.
Pretzels – GI score: 83
Pretzels may seem like a healthy snack, but they’re actually quite high in refined grains and carbohydrates. With a GI score of 83, they’re not the best choice for a quick snack or on-the-go bite. If you’re craving something salty, try roasted nuts or seeds instead.
Candy – GI score: varies
Candy comes in all shapes, sizes, and levels of sugar content. Depending on the type of candy, the GI score can vary. For example, gummy bears have a lower GI score (42) than jellybeans (80). If you’re craving something sweet, look for candies with lower sugar content or try fresh fruit instead.
Milkshake – GI score: 65
Milkshakes are a popular dessert option at many fast-food restaurants. However, their high sugar content earns them a GI score of 65. If you’re looking for a sweet treat, try a lower GI option like a fruit smoothie or some dark chocolate.
How Does the American Medical Association (AMA) View the Glycemic Index?
The American Medical Association recognizes the importance of the glycemic index in nutritional management. The organization confirms that the glycemic index is important in helping people maintain healthy diets.
Many studies conducted by the AMA suggest that low glycemic index diets can significantly improve glycemic control, particularly in diabetic patients.
They also support the use of the glycemic index to help individuals manage their blood sugar levels and reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The AMA recognizes the importance of low glycemic index foods, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables in promoting a healthy diet. They advocate for individuals to prioritize these low glycemic index foods in their diet plans.
The AMA stresses moderation in all dietary intake and they do not endorse one particular diet over another. They emphasize the importance of a balanced diet that includes the right mix of carbohydrates, fats, and protein to support a healthy lifestyle.
They are actively involved in researching the effects of glycemic index on weight loss and metabolic syndrome. They recognize that there is evidence suggesting that consuming a low glycemic index diet can help individuals with metabolic syndrome improve their blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
It’s worth noting that despite the recommended importance of the glycemic index, the final decision on dietary management should be left to the consumer or practitioner based on their individual condition and available nutritional information.

High Glycemic Foods to Avoid
Sugar and Sweets
Sugar and sweets are some of the most notorious ingredients when it comes to glycemic index. One tablespoon of sugar has a glycemic index of 65 while a can of soda has a GI of 80 or higher. Some alternative sweeteners such as agave, honey, and maple syrup may have lower GI values.
However, they are still high in fructose, low in nutrients, and can contribute to weight gain. If you have a sweet tooth, try sneaking in some fruits and berries into your diet as a natural alternative.
White Bread
White bread, like many refined grains, has a high glycemic index. Processed and refined carbs are quickly broken down by the body into simple sugars. White bread has a GI of around 75 which is why it is best to opt for whole-grain bread with a GI of around 50 or sprouted whole-grain bread which has even lower GIs.
Potatoes
Potatoes in various forms including chips, mashed, and fries can have high glycemic indexes. A baked potato, for example, has a GI of around 85-90 while mashed potatoes are estimated at 70 -80. So next time you are craving for potatoes, try sweet potatoes instead. They are loaded with fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and have a lower GI than regular potatoes.
Processed Foods
Most processed foods including canned foods, ready meals, and snacks have high glycemic index values because they contain not only refined carbs, but also high amounts of salt, sugar, and unhealthy fats.
According to research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, eating more processed foods was found to be linked with a higher risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
Breakfast Cereals
Most breakfast cereals are loaded with sugar which is one of the reasons they have high GI values. A common breakfast cereal can have a GI of around 80 which is higher than eating table sugar.
It is best to eat oatmeal or smoothie bowls at breakfast which are healthy, nutritious, low in GI, and provide your body with fiber that helps slow down digestion and makes you feel full longer.
Research reveals that consuming foods with a high Glycemic Index can lead to weight gain while eating foods with a low GI can aid in weight loss.
Contact us today
Email:
Phone: (346) 593-5619
Contact Human Resources Email:
Contact Operations Email:
Contact Authors for Her Weight Loss Email:
Customer Service Email:
Welcome to Her Weight Loss. We believe that a truly healthy lifestyle is within reach for everyone. Our team of award-winning experts has been dedicated to helping individuals achieve their ideal weight through our years of experience in the industry.
At Her Weight Loss, we understand that achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can be challenging. Our mission is to empower and support individuals on their journey towards a healthier self.
We strive to provide you with the most up-to-date knowledge-based tips and techniques for proper diet, nutrition, and exercise.
Our unique value proposition lies in our personalized approach towards weight loss. We recognize that each person’s body is different and requires specific attention. This is why we offer tailor-made solutions that cater to your individual needs for long-term success.
We are committed to building trust with our readers by providing reliable information backed by expertise and authoritative sources. You can count on us as your trusted partner in achieving your weight loss goals.